What is G-Code
G-Code is the fundamental programming language used to control CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools. Originating in the 1950s, G-Code was developed to provide a standardized way to direct automated machine tools, allowing precise control over movements and operations. This language uses simple, text-based commands to instruct CNC machines how to move, cut, drill, or mill parts with exact specifications.
In CNC operations, G-Code plays a critical role as the link between digital design and physical manufacturing. It translates CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models into actionable instructions that machines understand, enabling automation and high precision. Without G-Code, CNC machines cannot interpret design data or perform the detailed tasks required in modern manufacturing.
G-Code communicates with CNC machines by sending a sequence of commands that dictate tool movement, speed, and operation modes. Each line of G-Code directs the machine step-by-step, specifying coordinates, feed rates, and tool changes. This clear conversation between software and hardware ensures efficient, repeatable, and accurate machining processes across various industries.
Basics of G-Code in CNC Machine Tools
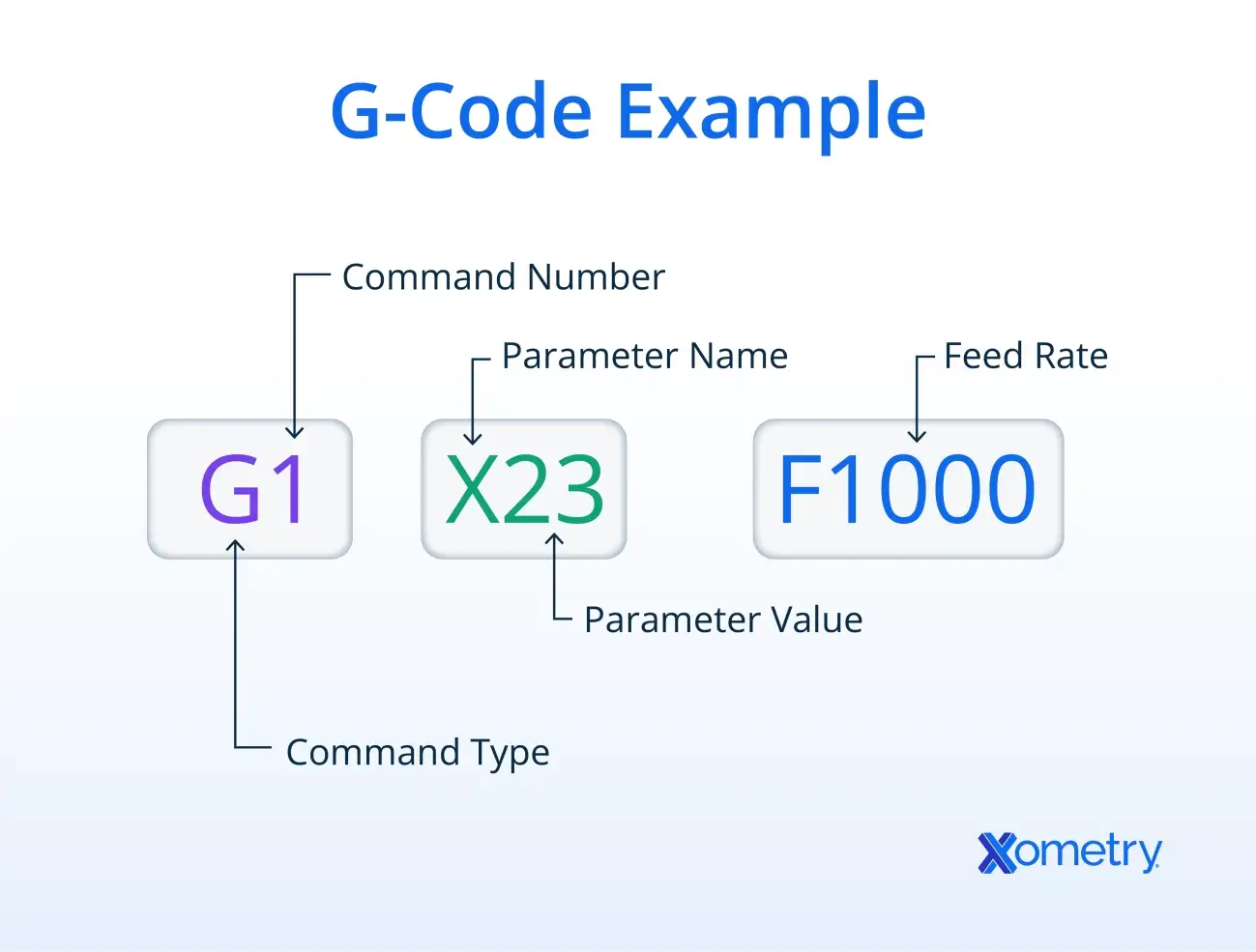
G-code commands follow a simple, organized format that CNC machines understand to perform precise movements. Each command usually starts with a letter followed by numbers—for example, G01 or M03. The letter indicates the type of action, like motion (G-codes) or machine control (M-codes), and the numbers specify the exact function.
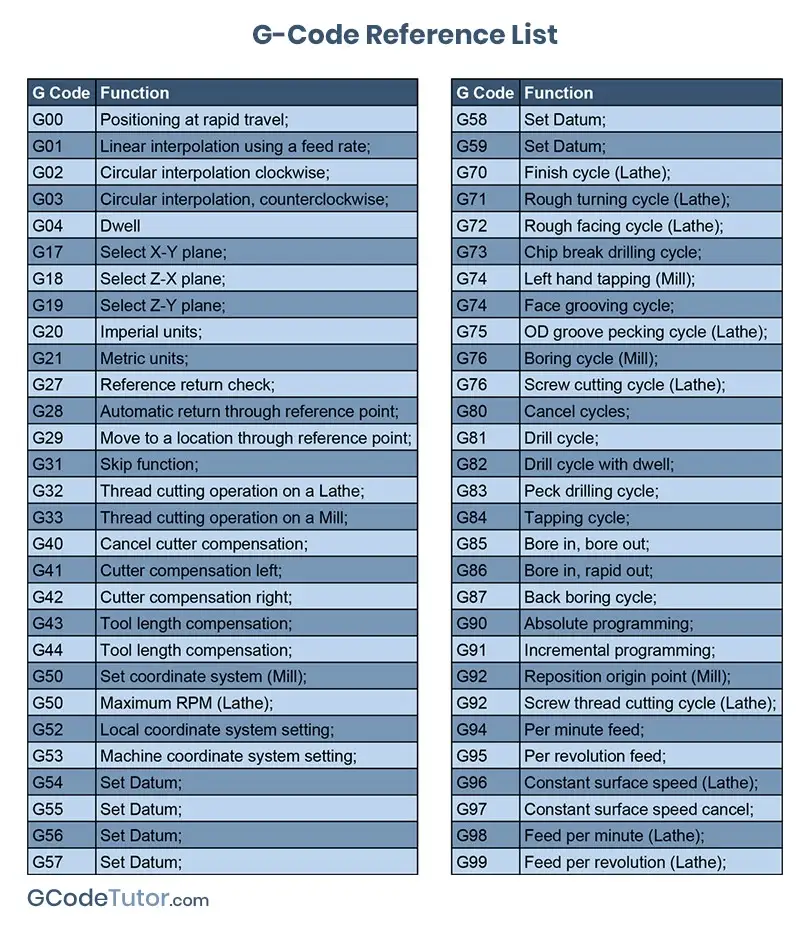
Here are some common G-code commands you’ll see in CNC programming:
- G00 – Rapid movement to a position without cutting (fast travel)
- G01 – Controlled, straight-line cutting at a set feed rate
- G02 – Circular interpolation clockwise (cutting in a circle clockwise)
- G03 – Circular interpolation counterclockwise
- M-codes – Control machine actions like spindle on/off (e.g., M03 starts the spindle)
Understanding how coordinates work is key to positioning tools correctly. CNC machines can use two types of coordinate systems:
- Absolute positioning (G90) – All movements reference a fixed point, usually the part origin. For example, if you tell the machine to move to X10 Y5, it moves to that exact point from the start.
- Incremental positioning (G91) – Movements are relative to the current tool location. So X10 Y5 means move 10 units right and 5 units forward from where the tool currently is.
How G-Code Works in CNC Machines
G-code is the bridge between your design and the actual machining process. It starts with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. You create a 3D model or 2D drawing in CAD, then use CAM software to generate the G-code. This code turns your design into step-by-step instructions that the CNC machine understands.
When the G-code is loaded into the CNC controller, the machine reads it line by line. Each command tells the machine how to move, what speed to use, when to turn the spindle on or off, and other essential functions. This precise communication ensures the finished part matches your design exactly.
Here’s a basic example of G-code snippet for a simple square:
G00 X0 Y0 ; Move quickly to the starting point (0,0)
G01 X50 Y0 F100 ; Cut in a straight line to (50,0) at feed rate 100
G01 X50 Y50 ; Cut straight up to (50,50)
G01 X0 Y50 ; Cut left to (0,50)
G01 X0 Y0 ; Cut down to the start point
M30 ; End of program
This example moves the tool around to cut a square shape. Understanding these commands helps you read or write G-code for simple parts, giving you control over how your CNC machine works.
Practical Applications of G-Code
G-code is the backbone of CNC machine automation and is widely used across various types of CNC machines. The main types include mills, lathes, and routers. Each uses G-code to control tool movements and machining processes precisely.
CNC Machines Using G-Code
- Mills: These machines cut and shape metal or other materials by moving a rotating cutting tool along multiple axes.
- Lathes: G-code controls the rotation of the workpiece and the cutting tool to perform turning operations.
- Routers: Mostly used for woodworking and plastics, routers follow G-code instructions to carve and cut shapes accurately.
Industries Benefiting from G-Code Programming
- Manufacturing: Automotive parts, aerospace components, and consumer electronics rely heavily on G-code for consistent quality and repeatability.
- Woodworking: Custom furniture and cabinetry makers use CNC routers programmed with G-code to speed up production and improve precision.
- Prototyping and Small-Batch Production: G-code allows quick changes in part designs, helping startups and small shops stay flexible.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: High precision G-code programming ensures tight tolerances critical for implants and prosthetics.
Impact on Precision, Speed, and Efficiency
G-code directly controls how a CNC machine moves and operates, which means it influences:
- Precision: G-code ensures exact positioning of tools, reducing human error and improving repeatability.
- Speed: Efficient G-code paths minimize time spent on non-cutting moves, speeding up the machining process.
- Machining Efficiency: Automated tool changes, spindle speed adjustments, and coordinated motions managed by G-code result in smoother operations and less waste.
Overall, mastering G-code is essential for anyone involved in CNC machining, whether you’re running a small local shop or managing a high-volume manufacturing facility in the U.S. It’s the key to unlocking accurate, fast, and efficient CNC production.
Writing and Editing G-Code Tips and Best Practices
Writing and editing G-code is a skill that improves with the right tools and a careful approach. To get started, most professionals use CAM software that generates G-code automatically from CAD designs. For manual tweaks or custom programs, simple text editors or specialized CNC code editing software work well. These tools help you write clear, error-free code and make quick changes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Programming G-Code
- Skipping comments: Always add comments for clarity to track what each block of code does.
- Incorrect coordinates: Mixing absolute and incremental positioning can cause tool crashes.
- Forgetting spindle or coolant commands: Ensure the M-codes for spindle speed and coolant are properly set.
- Ignoring machining limits: Verify axis travel limits to prevent crashes or damage.
- Overlooking tool changes: Program correct tool change commands to avoid unexpected tool paths.
Testing and Simulating G-Code
Before running your G-code on the actual CNC machine, simulation is key. Many CAM packages and dedicated CNC simulation software can preview the toolpath, catch errors, and optimize cutting sequences. Simulating helps:
- Avoid costly mistakes
- Check feed rates and speeds
- Optimize toolpaths for efficiency
By integrating proper tools, avoiding common coding errors, and thoroughly simulating your code first, you ensure safer and more efficient CNC machining.
For CNC beginners looking to practice with reliable machines, check out TechPro CNC’s ATC CNC Wood Router Machine TPM1325E that supports smooth G-code execution and easy programming.
Troubleshooting G-Code Errors
Working with G-code commands can sometimes lead to errors that stop your CNC machine from running smoothly. Common issues include syntax mistakes, incorrect coordinates, missing commands, or conflicts between G-code and M-code instructions.
Typical G-Code Errors
- Syntax errors: Typos or wrong code format
- Coordinate mistakes: Using wrong absolute vs incremental positioning
- Unsupported commands: Commands not compatible with your CNC machine model
- Tool path errors: Commands causing collisions or unexpected moves
- Missing M-codes: Forgetting machine start/stop or coolant commands
How to Debug and Fix Common Problems
- Review your code line by line: Look for misspellings and missing letters or numbers
- Use simulation software: Run your G-code in CAM simulators before machining
- Check coordinate references: Make sure you’re using absolute (G90) or incremental (G91) properly
- Validate tool paths: Verify there are no illegal or unsafe moves
- Refer to machine manuals: Match your codes with your CNC’s control system requirements
When to Seek Expert Help or Training
- If errors persist despite troubleshooting, it might be time to get hands-on training or expert advice. Mistakes in G-code can cause machine damage and wasted materials, so professional guidance from experienced CNC programmers or contacting a reliable provider like TechPro CNC can save time and money.
For quality CNC machines and expert guidance, explore options like automatic CNC wood cutting machines or other TechPro CNC resources to master proper programming and troubleshooting techniques.
Advanced G-Code Topics For Further Learning
Once you’re comfortable with basic G-code, it’s time to explore advanced concepts to boost your CNC machining skills. These include creating custom macros and subroutines, optimizing G-code for faster, more efficient runs, and understanding how different machine brands use unique dialects of G-code.
Custom Macros and Subroutines
Macros and subroutines allow you to reuse code snippets, reducing repetition and making your programs cleaner and easier to manage. For example, instead of rewriting the same drilling pattern multiple times, you can define it once as a subroutine and call it whenever needed. This saves time and cuts down on errors.
G-Code Optimization for Efficiency
Optimizing your G-code can make a noticeable difference in machining speed and tool life. Some common optimization tips include:
- Minimize rapid positioning moves (G00) that waste time.
- Use canned cycles for repetitive drilling or tapping to reduce code size.
- Smooth out toolpaths by properly sequencing operations to avoid unnecessary moves.
- Adjust feed rates and spindle speeds for different materials and tools.
Optimization helps maximize throughput and lowers wear on your CNC machine, making your runs smoother and more cost-effective.
Differences in G-Code Dialects Across Machine Brands
Not all CNC machines speak the exact same G-code language. Brands like Fanuc, Haas, Siemens, and others have variations in commands and syntax. Knowing these differences is key when switching machines or working with various CNC controllers.
| Brand | Unique G-Code Features | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fanuc | Common in US CNC machines, broad support | Standard G/M codes with some proprietary macros |
| Haas | User-friendly macros, specific M-codes | Popular in smaller shops |
| Siemens | Advanced subroutines, parametric programming | Strong in Europe, highly customizable |
Understanding these dialects allows you to write or modify code that works flawlessly on the target machine without costly errors or downtime.
If you want to dive deeper and master G-code for professional CNC machining or customize programs for your specific equipment, advanced training and hands-on experience are invaluable. Consider checking resources like TechPro CNC for expert guides and courses tailored to these advanced topics.
For businesses looking to upgrade or maintain CNC efficiency, proper G-code optimization paired with reliable machinery like our industrial CNC router machines can make a significant impact.
Why Choose TechPro CNC for CNC Training and Support
TechPro CNC stands out with deep expertise in CNC programming and hands-on training tailored to today’s machining needs. Whether you’re new to G-code or looking to sharpen your CNC skills, TechPro CNC offers clear, practical guidance that fits real-world applications.
What TechPro CNC Offers
-
Comprehensive Courses
Step-by-step CNC programming training, from G-code basics to advanced toolpath optimization.
-
Personalized Consultations
Expert help to troubleshoot your specific CNC challenges and optimize your machining process.
-
Expert Guides and Resources
Easy-to-follow manuals, sample G-code programs, and video tutorials designed for learners at all levels.
Why It Makes a Difference
TechPro CNC focuses on clear communication and practical skills that help you:
- Master CNC machine G-code commands quickly
- Avoid common programming mistakes
- Boost machining efficiency and precision
For anyone ready to get serious about CNC programming, connecting with TechPro CNC means access to the right knowledge and ongoing support.
Explore our lineup of 4-axis rotary CNC router machines and get a firsthand look at the tools you’ll master through their training.